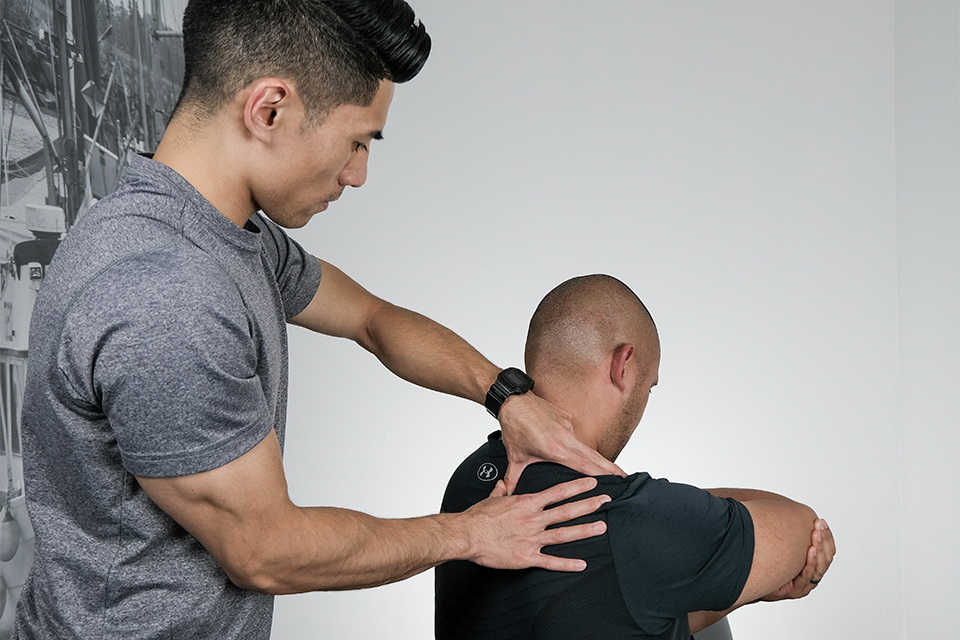
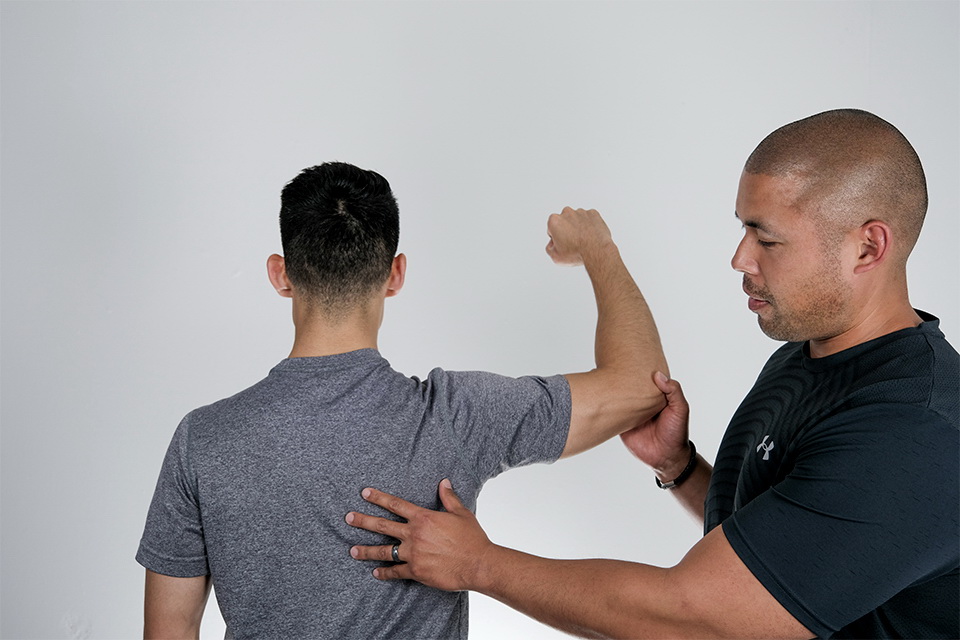
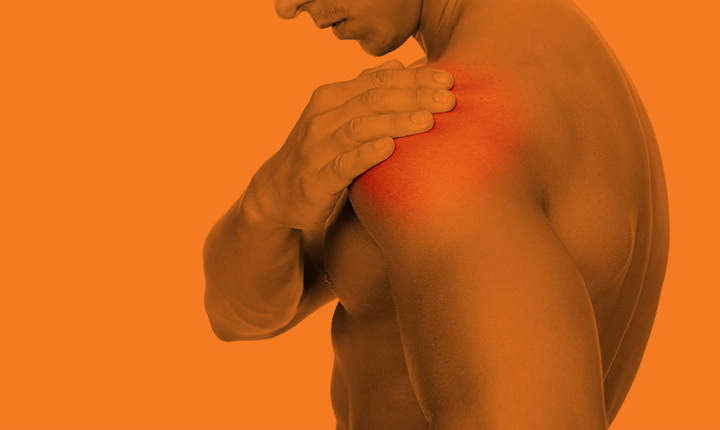
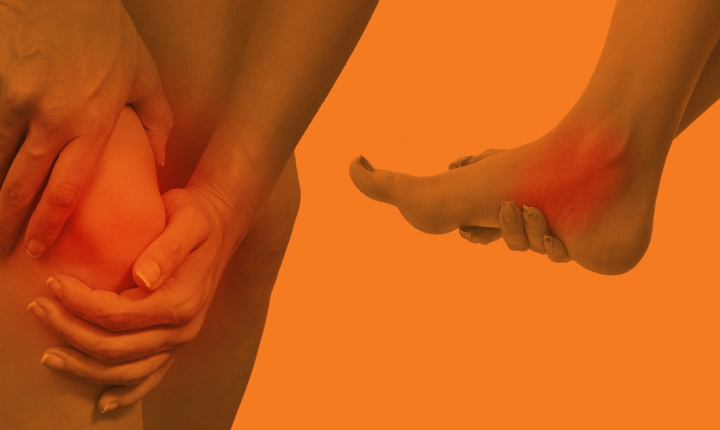
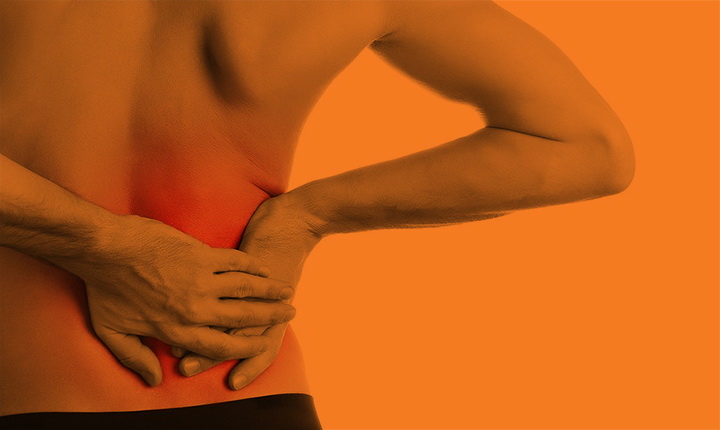
Our one-on-one treatment approach provides immediate relief to musculoskeletal injuries using a sports medicine model of rehabilitation to treat injuries sustained from sports or life.
We believe that the body functions as a whole.
Certified Athletic Therapists (A.T.) are highly skilled health care practitioners that provide immediate treatment to musculoskeletal injures and apply rehabilitation techniques to ensure a rapid return to work and play. A.T.'s employ a sports medicine model of rehabilitation to offer accelerated rehabilitation to physical injuries incurred from sports, recreation, daily activities or occupation.
An Athletic Therapist's training is focused in the area of assessment and rehabilitation of orthopedic conditions--the muscles, bones and joints. They can be found working closely with professional and national teams, and also in sports clinics across the country. Athletic Therapists are known for their aggressive treatment protocol in the attempt to speed up the healing process.
When Should I See An A.T.?
If you are an active individual and have a physical ailment that is either preventing you from continuing activity or feel that activity is causing your physical ailment, e.g. a runner experiencing chronic knee pain.
Athletic Therapy and Physiotherapy have similar skill sets when it comes to the assessment and treatment of orthopaedic injuries. The major differences between both health care professions is reflected in the training, techniques used for treatment and the scope of practice.
Registered Physiotherapists
Physiotherapists (P.T.) draw on similar training as Athletic Therapists in orthopaedics, but will be far more encompassing of all physical injuries. They are trained to assess and treat burn patients, people recovering from strokes, traumatic and congenital neurology as well as the elderly. Physiotherapists work in places such as private clinics, hospitals, and elderly care homes. Although some Physiotherapists offer treatments for sports injuries, not all Physiotherapists dedicate their full practice to the treatment and rehabilitation of these injuries like an Athletic Therapist.Athletic Therapy and Physiotherapy are two distinct professional designations and clients should check with their extended health care plans to see what professional designations are covered.
Knowing how Athletic Therapy and Physiotherapy work to promote healing will help you make a more confident decision about which treatment is best for you.
Our one-on-one treatment approach provides immediate relief to musculoskeletal injuries using a sports medicine model of rehabilitation to treat injuries sustained from sports or life.
We believe that the body functions as a whole.

Certified Athletic Therapists (A.T.) are highly skilled health care practitioners that provide immediate treatment to musculoskeletal injures and apply rehabilitation techniques to ensure a rapid return to work and play. A.T.'s employ a sports medicine model of rehabilitation to offer accelerated rehabilitation to physical injuries incurred from sports, recreation, daily activities or occupation.
An Athletic Therapist's training is focused in the area of assessment and rehabilitation of orthopedic conditions--the muscles, bones and joints. They can be found working closely with professional and national teams, and also in sports clinics across the country. Athletic Therapists are known for their aggressive treatment protocol in the attempt to speed up the healing process.
When Should I See An A.T.?
If you are an active individual and have a physical ailment that is either preventing you from continuing activity or feel that activity is causing your physical ailment, e.g. a runner experiencing chronic knee pain.
Knowing how Athletic Therapy and Physiotherapy work to promote healing will help you make a more confident decision about which treatment is best for you.

Athletic Therapy and Physiotherapy have similar skill sets when it comes to the assessment and treatment of orthopaedic injuries. The major differences between both health care professions is reflected in the training, techniques used for treatment and the scope of practice.
Registered Physiotherapists
Physiotherapists (P.T.) draw on similar training as Athletic Therapists in orthopaedics, but will be far more encompassing of all physical injuries. They are trained to assess and treat burn patients, people recovering from strokes, traumatic and congenital neurology as well as the elderly. Physiotherapists work in places such as private clinics, hospitals, and elderly care homes. Although some Physiotherapists offer treatments for sports injuries, not all Physiotherapists dedicate their full practice to the treatment and rehabilitation of these injuries like an Athletic Therapist.Athletic Therapy and Physiotherapy are two distinct professional designations and clients should check with their extended health care plans to see what professional designations are covered.
Our one-on-one treatment approach provides immediate relief to musculoskeletal injuries using a sports medicine model of rehabilitation to treat injuries sustained from sports or life.
We believe that the body functions as a whole.

Certified Athletic Therapists (A.T.) are highly skilled health care practitioners that provide immediate treatment to musculoskeletal injures and apply rehabilitation techniques to ensure a rapid return to work and play. A.T.'s employ a sports medicine model of rehabilitation to offer accelerated rehabilitation to physical injuries incurred from sports, recreation, daily activities or occupation.
An Athletic Therapist's training is focused in the area of assessment and rehabilitation of orthopedic conditions--the muscles, bones and joints. They can be found working closely with professional and national teams, and also in sports clinics across the country. Athletic Therapists are known for their aggressive treatment protocol in the attempt to speed up the healing process.
When Should I See An A.T.?
If you are an active individual and have a physical ailment that is either preventing you from continuing activity or feel that activity is causing your physical ailment, e.g. a runner experiencing chronic knee pain.
Knowing how Athletic Therapy and Physiotherapy work to promote healing will help you make a more confident decision about which treatment is best for you.

Athletic Therapy and Physiotherapy have similar skill sets when it comes to the assessment and treatment of orthopaedic injuries. The major differences between both health care professions is reflected in the training, techniques used for treatment and the scope of practice.
Registered Physiotherapists
Physiotherapists (P.T.) draw on similar training as Athletic Therapists in orthopaedics, but will be far more encompassing of all physical injuries. They are trained to assess and treat burn patients, people recovering from strokes, traumatic and congenital neurology as well as the elderly. Physiotherapists work in places such as private clinics, hospitals, and elderly care homes. Although some Physiotherapists offer treatments for sports injuries, not all Physiotherapists dedicate their full practice to the treatment and rehabilitation of these injuries like an Athletic Therapist.Athletic Therapy and Physiotherapy are two distinct professional designations and clients should check with their extended health care plans to see what professional designations are covered.
Our one-on-one treatment approach provides immediate relief to musculoskeletal injuries using a sports medicine model of rehabilitation to treat injuries sustained from sports or life.
We believe that the body functions as a whole.

Certified Athletic Therapists (A.T.) are highly skilled health care practitioners that provide immediate treatment to musculoskeletal injures and apply rehabilitation techniques to ensure a rapid return to work and play. A.T.'s employ a sports medicine model of rehabilitation to offer accelerated rehabilitation to physical injuries incurred from sports, recreation, daily activities or occupation.
An Athletic Therapist's training is focused in the area of assessment and rehabilitation of orthopedic conditions--the muscles, bones and joints. They can be found working closely with professional and national teams, and also in sports clinics across the country. Athletic Therapists are known for their aggressive treatment protocol in the attempt to speed up the healing process.
When Should I See An A.T.?
If you are an active individual and have a physical ailment that is either preventing you from continuing activity or feel that activity is causing your physical ailment, e.g. a runner experiencing chronic knee pain.

Knowing how Athletic Therapy and Physiotherapy work to promote healing will help you make a more confident decision about which treatment is best for you.
Athletic Therapy and Physiotherapy have similar skill sets when it comes to the assessment and treatment of orthopaedic injuries. The major differences between both health care professions is reflected in the training, techniques used for treatment and the scope of practice.
Registered Physiotherapists
Physiotherapists (P.T.) draw on similar training as Athletic Therapists in orthopaedics, but will be far more encompassing of all physical injuries. They are trained to assess and treat burn patients, people recovering from strokes, traumatic and congenital neurology as well as the elderly. Physiotherapists work in places such as private clinics, hospitals, and elderly care homes. Although some Physiotherapists offer treatments for sports injuries, not all Physiotherapists dedicate their full practice to the treatment and rehabilitation of these injuries like an Athletic Therapist.Athletic Therapy and Physiotherapy are two distinct professional designations and clients should check with their extended health care plans to see what professional designations are covered.
There are three key areas of recovery
where Athletic Therapy is optimal:
Prevention includes musculoskeletal and postural evaluation, equipment selection, fitting and repair, warm-up, conditioning programs, prophylactic or supportive taping, and adapting to the activity environment and facilities.
Immediate care of athletic injuries includes: injury assessment, basic emergency life support, recognition and management of acute traumatic neurological dysfunction, provision of first aid, preparation for entrance into appropriate health care delivery systems, or, where appropriate, utilization of techniques facilitating a safe return to participation.
Certified Athletic Therapists assess injuries and conditions, use contemporary rehabilitative techniques, therapeutic modalities, soft tissue mobilization, physical reconditioning, and supportive strapping procedures to promote an environment conducive to optimal healing in preparing individuals for safe reintegration into an active lifestyle.
There are three key areas of recovery where Athletic Therapy is optimal:
Prevention includes musculoskeletal and postural evaluation, equipment selection, fitting and repair, warm-up, conditioning programs, prophylactic or supportive taping, and adapting to the activity environment and facilities.
Immediate care of athletic injuries includes: injury assessment, basic emergency life support, recognition and management of acute traumatic neurological dysfunction, provision of first aid, preparation for entrance into appropriate health care delivery systems, or, where appropriate, utilization of techniques facilitating a safe return to participation.
Certified Athletic Therapists assess injuries and conditions, use contemporary rehabilitative techniques, therapeutic modalities, soft tissue mobilization, physical reconditioning, and supportive strapping procedures to promote an environment conducive to optimal healing in preparing individuals for safe reintegration into an active lifestyle.
There are three key areas of recovery
where Athletic Therapy is optimal:
Prevention includes musculoskeletal and postural evaluation, equipment selection, fitting and repair, warm-up, conditioning programs, prophylactic or supportive taping, and adapting to the activity environment and facilities.
Immediate care of athletic injuries includes: injury assessment, basic emergency life support, recognition and management of acute traumatic neurological dysfunction, provision of first aid, preparation for entrance into appropriate health care delivery systems, or, where appropriate, utilization of techniques facilitating a safe return to participation.
Certified Athletic Therapists assess injuries and conditions, use contemporary rehabilitative techniques, therapeutic modalities, soft tissue mobilization, physical reconditioning, and supportive strapping procedures to promote an environment conducive to optimal healing in preparing individuals for safe reintegration into an active lifestyle.
There are three key areas of recovery where Athletic Therapy is optimal:
Prevention includes musculoskeletal and postural evaluation, equipment selection, fitting and repair, warm-up, conditioning programs, prophylactic or supportive taping, and adapting to the activity environment and facilities.
Immediate care of athletic injuries includes: injury assessment, basic emergency life support, recognition and management of acute traumatic neurological dysfunction, provision of first aid, preparation for entrance into appropriate health care delivery systems, or, where appropriate, utilization of techniques facilitating a safe return to participation.
Certified Athletic Therapists assess injuries and conditions, use contemporary rehabilitative techniques, therapeutic modalities, soft tissue mobilization, physical reconditioning, and supportive strapping procedures to promote an environment conducive to optimal healing in preparing individuals for safe reintegration into an active lifestyle.
Rehabilitative exercise during the treatment is important in helping your body reconnect mind to muscle and repattern the musculature around the injury. While we try to spend most of the treatment time hands on, we expect the patient to comply with exercises post treatment.
If it is a chronic injury that you are dealing with, imagine that all your daily activities (driving, sitting at desk, sleeping on one side) have led you to this state of physical pain. Therefore you must take on a daily change to break the cycle of dysfunction that your body gets into.
Whether it is 2-4 minutes of stretching and exercise a day or getting up for a walk around the office every hour. It is important to incorporate rehabilitation exercises into your daily schedule.
Rehabilitative exercise during the treatment is important in helping your body reconnect mind to muscle and repattern the musculature around the injury. While we try to spend most of the treatment time hands on, we expect the patient to comply with exercises post treatment.
If it is a chronic injury that you are dealing with, imagine that all your daily activities (driving, sitting at desk, sleeping on one side) have led you to this state of physical pain. Therefore you must take on a daily change to break the cycle of dysfunction that your body gets into.
Whether it is 2-4 minutes of stretching and exercise a day or getting up for a walk around the office every hour. It is important to incorporate rehabilitation exercises into your daily schedule.
Rehabilitative exercise during the treatment is important in helping your body reconnect mind to muscle and repattern the musculature around the injury. While we try to spend most of the treatment time hands on, we expect the patient to comply with exercises post treatment.
If it is a chronic injury that you are dealing with, imagine that all your daily activities (driving, sitting at desk, sleeping on one side) have led you to this state of physical pain. Therefore you must take on a daily change to break the cycle of dysfunction that your body gets into.
Whether it is 2-4 minutes of stretching and exercise a day or getting up for a walk around the office every hour. It is important to incorporate rehabilitation exercises into your daily schedule.
Rehabilitative exercise during the treatment is important in helping your body reconnect mind to muscle and repattern the musculature around the injury. While we try to spend most of the treatment time hands on, we expect the patient to comply with exercises post treatment.
If it is a chronic injury that you are dealing with, imagine that all your daily activities (driving, sitting at desk, sleeping on one side) have led you to this state of physical pain. Therefore you must take on a daily change to break the cycle of dysfunction that your body gets into.
Whether it is 2-4 minutes of stretching and exercise a day or getting up for a walk around the office every hour. It is important to incorporate rehabilitation exercises into your daily schedule.
Understanding how the musculoskeletal system works together allows us to treat the whole body and promote a healthy and speedy recovery. Below are a few common cases that can be treated with Athletic Therapy.
Understanding how the musculoskeletal system works together allows us to treat the whole body and promote a healthy and speedy recovery. Below are a few common cases that can be treated with Athletic Therapy.
Understanding how the musculoskeletal system works together allows us to treat the whole body and promote a healthy and speedy recovery. Below are a few common cases that can be treated with Athletic Therapy.
Understanding how the musculoskeletal system works together allows us to treat the whole body and promote a healthy and speedy recovery. Below are a few common cases that can be treated with Athletic Therapy.
© Copyright Evolution Sport Therapy 2025.
Newsletter Signup
Sign up for our newsletter to receive all the latest!
Newsletter Signup
Sign up for our newsletter to receive all the latest!
© Copyright Evolution Sport Therapy 2025.
Newsletter Signup
Sign up for our newsletter to receive all the latest!
© Copyright Evolution Sport Therapy 2025.